
The free, open-source content management system WordPress is one of the most popular systems of this Internet era. With more than 66 million installations and a market share of around 66%, it is one of the most important and best systems in the field of content management systems. However, with its popularity comes a high risk of cyber attacks from hackers and malware. It is crucial to secure your WordPress site from these security threats to protect your website and your users’ data.
I will guide you on how to secure your WordPress site from hackers and malware.
1. Keep your WordPress site updated
The first step in securing your WordPress site is to keep it updated. This includes the WordPress core, themes, and plugins. WordPress releases regular updates to address security vulnerabilities and bugs. By keeping your WordPress site updated, you ensure that you have the latest security patches and fixes.
To update your WordPress site, log in to your WordPress admin panel and navigate to the Dashboard. If there is an update available, you will see a notification in the Updates section. Click on the update button to update your site.
2. Use strong passwords
Using strong passwords is another crucial step in securing your WordPress site. A weak password makes it easy for hackers to gain access to your site. It is essential to use strong, unique passwords for your WordPress admin account and all other user accounts on your site. Also, consider using a password manager to keep track of your passwords.
A strong password should have at least eight characters, including uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable passwords such as “123456” or “password.”
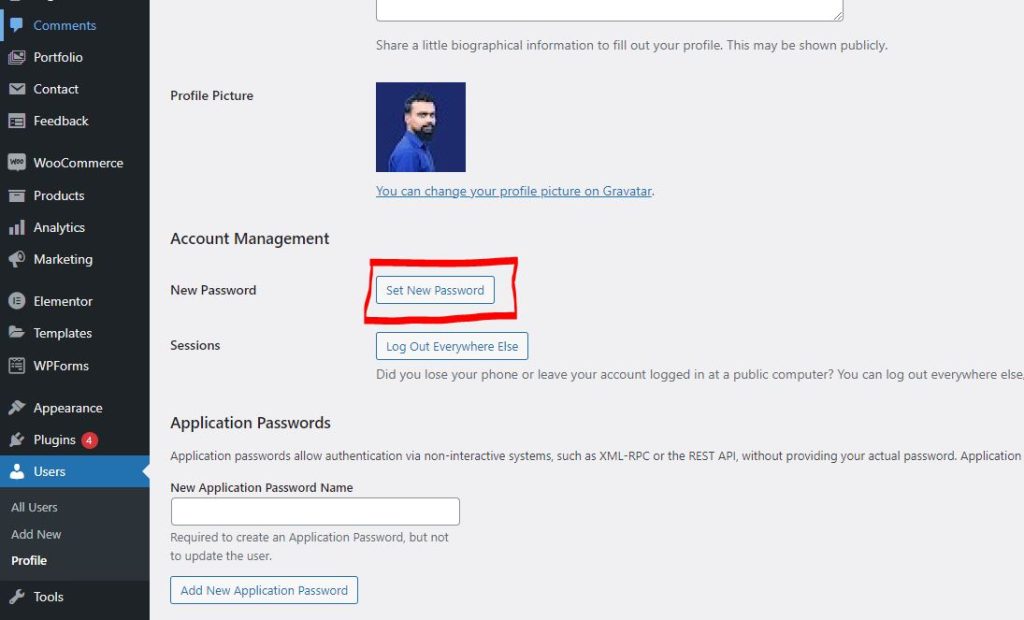
To change your password in WordPress, navigate to Users > Your Profile. Scroll down to the Account Management section, where you can change your password.
3. Install security plugins
Installing a reputable security plugin is an effective way to protect your WordPress site from malware and brute-force attacks. There are several security plugins available for WordPress, including Wordfence, Sucuri, and iThemes Security.
These security plugins offer features such as malware scanning, firewall protection, brute-force protection, and two-factor authentication (2FA). They also provide real-time alerts in case of security threats and vulnerabilities.
To install a security plugin, log in to your WordPress admin panel and navigate to Plugins > Add New. Search for the security plugin you want to install, and click on the install button. Once the plugin is installed, activate it and follow the setup wizard.
4. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your WordPress site by requiring users to enter a unique code in addition to their password to access your site. This ensures that only authorized users can log in to your site.
There are several WordPress plugins that offer 2FA, including Google Authenticator, Duo Two-Factor Authentication, and Two-Factor Authentication. Once you install a 2FA plugin, you can configure it in the plugin settings.
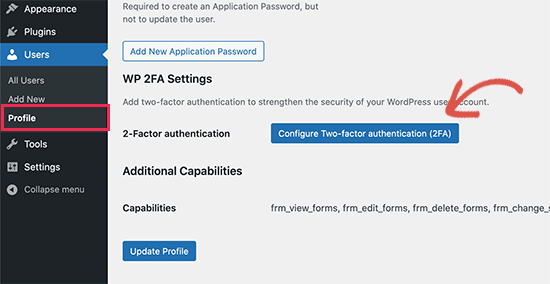
To enable 2FA in WordPress, log in to your WordPress admin panel and navigate to Users > Your Profile. Scroll down to the Two-Factor Options section and follow the instructions to enable 2FA.
5. Use HTTPS
Using HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) adds an additional layer of security to your WordPress site by encrypting data transmitted between your users’ browsers and your server. This prevents hackers from intercepting sensitive data such as login credentials, credit card information, and personal data.
To enable HTTPS on your WordPress site, you need an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate. You can obtain an SSL certificate from your web host or a third-party SSL provider. Once you have an SSL certificate, you can install it on your WordPress site.
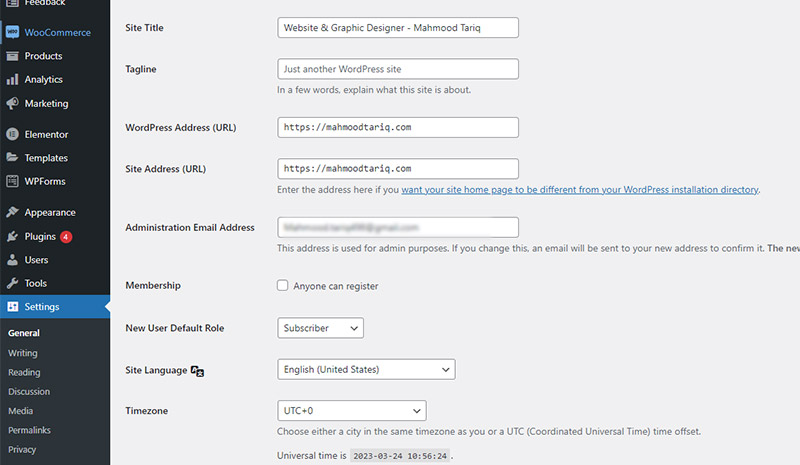
To enable HTTPS in WordPress, log in to your WordPress admin panel and navigate to Settings > General. Change the WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) to use HTTPS instead
7. Limit login attempts
Limit the number of login attempts allowed on your WordPress site to prevent brute-force attacks.
8. Regularly backup your site
Having a backup of your WordPress site is crucial in case of any security breach or data loss. Not having a proper backup plan in place can lead to loss of data, prolonged downtime, and even loss of revenue.
To fix this issue, it’s important to regularly back up your WordPress site.
